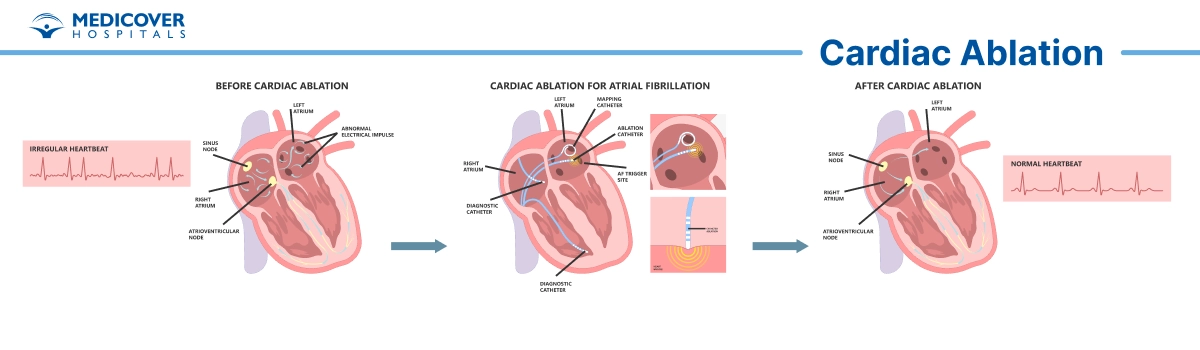
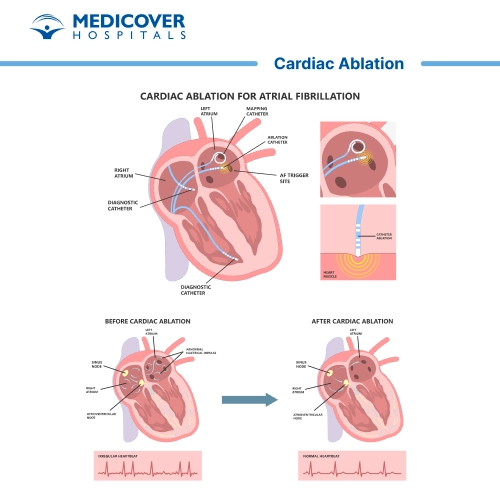
Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to treat abnormal heart rhythms, also known as arrhythmias. It involves targeting and destroying small areas of heart tissue that are causing irregular electrical signals. This procedure is often recommended when medicines fail to control symptoms or when the arrhythmia poses serious health risks.
Cardiac ablation is also called catheter ablation. It is performed by inserting thin, flexible catheters through blood vessels into the heart. Radiofrequency energy or cryotherapy is then used to destroy or ablate the infected tissue.
Who is a Candidate for Cardiac Ablation?
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib): An irregular heartbeat in the upper chambers. Ablation restores normal rhythm when medications fail.
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): Rapid heart rhythms above the ventricles. Ablation corrects abnormal electrical pathways.
- Atrial flutter: A regular, organized fast rhythm in the heart's upper chambers.
- Accessory Pathways: Extra pathways cause arrhythmias like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Ablation removes them.
- Ventricular tachycardia: Rapid heartbeat in the lower chambers. Ablation treats certain types.
- Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT): Abnormal pathways causing SVT. Ablation eliminates these.
- Other symptomatic arrhythmias not controlled by medication.
Key Takeaways
- Type of Procedure: Minimally invasive (catheter-based).
- Duration: 2 to 4 hours on average.
- Anesthesia Used: Local anesthesia with conscious sedation or general anesthesia.
- Recovery Time: Most patients return to normal activities within 1 week.
- Success Rate: 70% to 95%, depending on the type of arrhythmia.
Types of Cardiac Ablation
- Catheter Ablation: A catheter delivers energy to problematic heart tissue.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Uses radiofrequency energy to destroy tissue.
- Cryoablation: Freezes abnormal tissue to restore rhythm.
- Laser Ablation: Laser energy destroys abnormal tissue.
- Surgical Ablation: Performed during heart surgery for complex cases.
Indications of Cardiac Ablation
Cardiac(Heart) ablation is recommended for individuals with specific types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) that haven't responded well to medications or other treatments. Common indications include:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): An irregular heartbeat in the upper chambers of the heart. Ablation restores normal rhythm when medications fail.
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): Rapid heart rhythms above the ventricles. Ablation corrects abnormal electrical pathways.
- Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Ventricular tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat in the lower chambers. Ablation treats certain types of VT.
- Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT): Abnormal pathways causing SVT. Ablation eliminates these pathways.
- Accessory Pathways: Extra electrical pathways cause arrhythmias like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Ablation removes them.
- Ventricular Fibrillation Risk: Ablation may reduce the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation.
Common arrhythmias treated include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, SVT, and ventricular tachycardia.
Post-Cardiac Ablation Symptoms
- Mild chest discomfort
- Fatigue
- Temporary palpitations
- Bruising at catheter sites
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionPreparing for Cardiac Ablation Surgery
Preparing for cardiac ablation surgery involves several important steps to ensure a safe and successful procedure. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to prepare:
- Consultation: Meet with a cardiac electrophysiologist to discuss your condition and treatment options.
- Medical Evaluation: Complete necessary tests and imaging to assess your health.
- Medication Review: Give a list of all medications, and follow guidelines about what to hold in advance of the procedure.
- Fasting: Follow fasting instructions; typically, no food or drink after midnight.
- Transportation: Have someone available to drive you to and from the hospital.
- Stop Smoking: If you smoke, make an effort to quit or reduce before the process.
- Hygiene: Take a shower prior to the procedure to reduce the risk of infection.
- Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothes; bring only essentials.
- Medication Instructions: Follow your doctor's guidance on medications.
- Consent Forms: Sign any necessary forms after understanding the procedure.
- Mental Preparation: Understand the procedure and potential outcomes.
Who Will Perform the Cardiac Ablation Procedure?
Cardiac ablation is a specialized procedure performed by a cardiac electrophysiologist. A cardiologist who has undergone additional training and expertise in the field of electrophysiology, which focuses on the electrical activities of the heart and the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias.
These highly trained medical professionals have extensive knowledge of the heart's electrical system, various arrhythmias, and techniques used in cardiac ablation procedures.
What Happens During the Cardiac Catheter Ablation Procedure?
During a cardiac ablation procedure, several steps are taken to diagnose and treat abnormal heart rhythms, also known as arrhythmias. Here's an overview of what happens during a cardiac ablation:
- Patient Evaluation: Medical history and tests, such as an ECG, are reviewed to identify cardiac arrhythmia.
- Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia or mild sedation is given for comfort.
- Catheter Insertion: A thin catheter is inserted through a blood vessel to the heart.
- Mapping: Catheters record the heart's electrical activity to locate abnormal signals.
- Energy Application: Radiofrequency or cryotherapy energy is applied to disrupt faulty electrical pathways.
- Monitoring: Heart rhythm is monitored throughout to ensure successful treatment.
- Verification: The medical team checks if the arrhythmia is corrected after each energy application.
- Completion: Once the arrhythmia is corrected, catheters are removed.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Benefits and Risks of Cardiac Ablation Procedure
Benefits
- Reduces/eliminates arrhythmia symptoms (palpitations, dizziness).
- Improves quality of life.
- May reduce long-term medication needs.
- Decreases stroke/heart failure risk.
Risks
- Vascular injury
- Heart puncture/tamponade
- Stroke/heart attack
- Allergic reactions
- Pulmonary vein stenosis
- Arrhythmia recurrence
- Bleeding/infection at the catheter site
Recovery After a Cardiac Ablation Procedure
Recovery after a cardiac ablation procedure is a gradual process that involves rest, monitoring, and adherence to your medical team's postoperative instructions. The duration and specifics of your recovery can vary based on the type of arrhythmia treated, your overall health, and the approach used during the procedure.
Here's what you can generally expect during the recovery period:
- Immediate Recovery: Monitor the recovery area; dressings are applied.
- Observation: Vital signs/heart rhythm monitored for hours/overnight.
- Pain & Discomfort: Mild soreness treated with OTC painkillers.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting for days.
- Follow-up Appointments: Track recovery and adjust medications.
- Wound Care: Keep catheter sites clean/dry.
- Resuming Activities: Light activities in days; strenuous exercise after 1 to 2 weeks.
- Contact Medical Team: If experiencing bleeding, infection, chest pain, or irregular heartbeats.
Lifestyle Changes After Cardiac Ablation Procedure
After a cardiac ablation procedure, lifestyle changes can contribute to your overall heart health, promote healing, and decrease the risk of future heart rhythm issues.
Here are some lifestyle changes to consider:
- Stick to medication and activity recommendations.
- Choose fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Engage in moderate activities like walking or swimming.
- Try yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Healthy diet and exercise.
- Smoking harms heart health and hinders lung healing.
- Drink in moderation. Keep levels in check.
- Control blood sugar with diet and medication.
- Aim for quality sleep.
- Prevent infections by staying clean.
- Take medications as prescribed.
- Keep track of your progress with your doctor.
- Rely on family and friends for emotional support.