Craniotomy surgery is a complex and specialized neurosurgical procedure that involves carefully opening the skull to access the brain. It is a crucial technique to diagnose and treat neurological conditions, including brain tumours, vascular abnormalities, traumatic brain injuries, and epileptic seizures.
This procedure allows neurosurgeons to interact directly with the brain tissue, enabling precise interventions and treatments that significantly improve the patient's quality of life and chances of recovery.
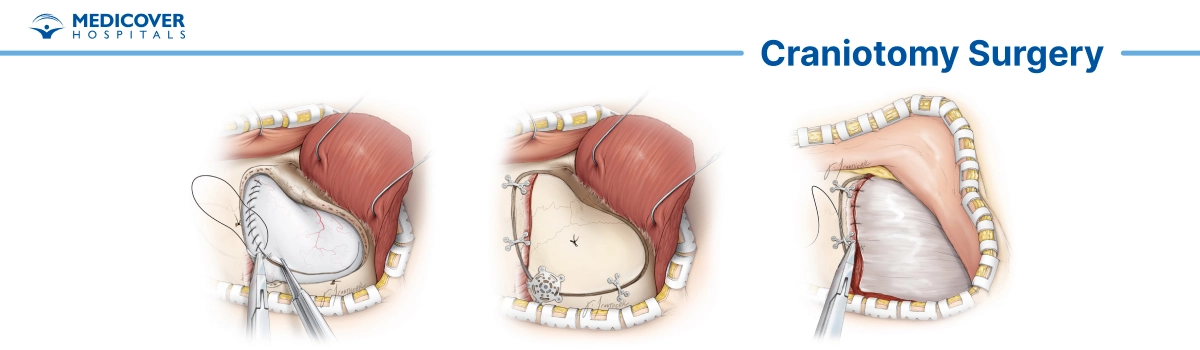
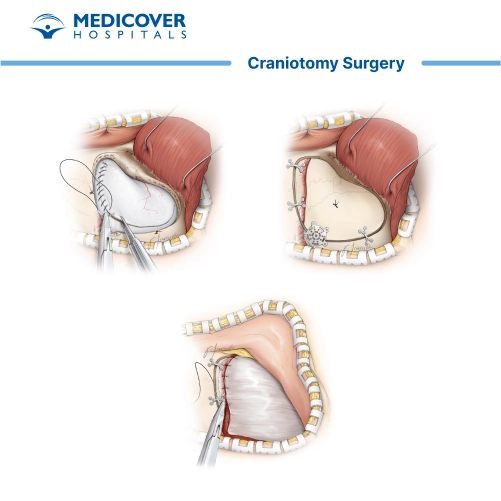
Craniotomy Surgery: Key Takeaways
- Type of Procedure: Invasive surgical procedure
- Duration: Typically 3 to 5 hours, depending on the condition being treated
- Anesthesia Used: General anesthesia
- Recovery Time: Initial hospital stay of 3 to 7 days; full recovery may take several weeks to a few months, depending on the case
Types of Craniotomy
Craniotomy types vary based on the surgical approach and purpose. Common types include:
- Frontal Craniotomy: accesses the front part of the brain for the removal of tumors or treatment of trauma.
- Temporal Craniotomy: Performed on the temporal lobe to treat epilepsy, tumors, or vascular conditions.
- Parietal Craniotomy: Targets the parietal region for tumor removal or neurological disorders.
- Occipital Craniotomy: Focuses on the occipital lobe, often for vision-related issues or tumors.
- Pterional (Frontotemporal) Craniotomy: A standard approach for aneurysm repair, tumors, and vascular lesions.
- Suboccipital Craniotomy: Used to access the cerebellum and brainstem, often for Chiari malformation or posterior fossa tumors.
- Orbitozygomatic Craniotomy: A complex technique that removes parts of the skull for deep brain access, typically for large tumors.
- Keyhole Craniotomy: A minimally invasive approach for small tumors or biopsies with less recovery time.
- Awake Craniotomy: Performed while the patient is awake to monitor brain function, often used for epilepsy or tumor removal near critical areas.
Each type is chosen based on the condition being treated and the location of the affected brain area.
Indications for Craniotomy Surgery
- Brain Tumors: Craniotomy is often performed to remove benign or malignant brain tumours.;
- Aneurysms and Vascular Abnormalities: Craniotomy surgery may be used to clip or remove aneurysms, address AVMs, and restore normal blood flow surgically.
- Traumatic Brain Injuries: Severe head injuries can lead to bleeding, swelling, or the formation of blood clots in the brain.
- Epilepsy Surgery: In cases of drug-resistant epilepsy, a craniotomy may be performed to identify and resect the specific brain tissue causing seizures.
- Hydrocephalus: Creating an opening to drain excess fluid or implanting a shunt system to divert fluid from the brain.
- Stroke and Vascular Lesions: Managing complications from strokes, cavernous malformations, or arteriovenous fistulas.
- Biopsy: Removal of brain tissue samples for accurate diagnosis of unexplained neurological symptoms.
- Cranial Nerve Disorders: Decompression of nerves affected by conditions like trigeminal neuralgia or hemifacial spasm.
- Cerebral Abscesses: Drainage and removal of brain abscesses resulting from infection.
- Revascularization Procedures: Improving blood flow in cases like Moyamoya disease by creating new vascular pathways.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionWho Performs the Craniotomy Procedure?
Craniotomy is performed by a neurosurgeon, a medical doctor specialized in diagnosing and surgically treating conditions of the brain, spine, and nervous system. The neurosurgeon works closely with a team that may include neurologists, anesthesiologists, radiologists, and critical care specialists to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Preparing for Craniotomy surgery
Preparing for craniotomy surgery involves several steps to ensure that the patient and the medical team are well-equipped. Following your healthcare provider's instructions closely and communicating concerns is essential. Here are some general guidelines on how to prepare for craniotomy surgery:
- Medical Consultation: Your neurosurgeon will conduct a thorough evaluation of your medical history, perform physical examinations, and review any imaging studies (MRI, CT scans) to determine the need for surgery and the best approach. Be sure to provide accurate information about your medical history, medications, allergies, and any past surgeries.
- Discussion and Informed Consent: Your surgeon will discuss the details of the procedure, including its purpose, potential risks, benefits, and alternatives. Ask questions to clarify any doubts or concerns. You'll be asked to provide informed consent once you understand the procedure and its implications.
- Preoperative Testing: Your medical team may order blood tests, an ECG, chest X-rays, or other tests to assess your overall health and ensure you are physically ready for surgery.
- Medications: Your surgeon will provide instructions on which medications to continue taking and which to stop temporarily before the surgery. This may include blood-thinning medications, herbal supplements, and non-prescription drugs.
- Fasting: You will likely be instructed to fast (avoid eating and drinking) for a specific duration before the surgery. Follow the fasting instructions provided by your medical team to minimize the risk of complications during anaesthesia.
- Hygiene: Shower or bathe with an antibacterial soap the night before or in the morning of the surgery. This helps reduce the risk of infection.
Steps Involved In the Craniotomy Surgery Procedure
During a craniotomy operation, several key steps are involved to safely and effectively access the brain, address neurological issues, and promote the patient's recovery. Here is an overview of what happens during a craniotomy procedure:
- Preoperative Assessment and Planning: Before surgery, the medical team reviews the patient's medical history and imaging scans, such as MRI and CT scans, and conducts various tests to assess their overall health and suitability for surgery. The surgical team determines the location and size of the incision, as well as the specific approach to access the target brain area.
- Anesthesia Administration: The patient is administered general anaesthesia, ensuring they are unconscious and pain-free during the surgery. An anesthesiologist monitors the patient's vital signs throughout the procedure.
- Incision and Bone Flap Removal: The surgeon makes a precise incision on the scalp over the designated area of the skull. The skin and underlying tissues are carefully moved aside to expose the skull. A specialized drill or saw is then used to create a bone flap, a section of the head that is temporarily removed to access the brain.
- Brain Exposure: With the bone flap removed, the underlying layers of protective tissue (dura mater) are gently opened to expose the brain. This provides direct access to the affected area.
- Surgical Intervention: Depending on the purpose of the surgery, the surgeon performs specific procedures. This may include removing brain tumours, addressing vascular abnormalities (aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations), relieving pressure from traumatic brain injuries or swelling, resecting epileptic foci, and more. Advanced surgical tools and techniques, such as microscopes and neuronavigation systems, are often utilized for precision.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Recovery After Craniotomy surgery
Post-craniotomy surgery is a gradual process that involves physical healing, psychological adjustment, and a tailored rehabilitation plan. The duration and specifics of the recovery period can vary based on the type of surgery, the underlying condition, and individual factors. Here's an overview of what to expect during the recovery phase:
- Monitoring: In the PACU, vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, breathing) are monitored to provide pain relief.
- Stay in the Hospital: Varies according to recovery. Monitoring and care provided.
- Pain: Medications were administered; discomfort improved progressively.
- Activity: Start ambulating early. When indicated, move to sitting, ambulation, and light activity.
- Nutrition: Eat and drink plenty of water to help you heal.
- Wound Care: Follow instructions for keeping the incision clean and dry.
- Follow-ups: Go to appointments where healing and recovery are monitored.
- Rehabilitation: You may need therapy to help you regain strength or function.
- Psychological Recovery: Irritability, sadness, and anxiety are normal reactions; get support.
- Resumption of regular activities: Return to usual routine slowly, as recommended.
Long-Term Side Effects and Complications of a Craniotomy
The long-term side effects of a craniotomy depend on the underlying condition, the complexity of the procedure, and an individual's healing process. Possible effects include:
- Cognitive Impairment: Memory issues, difficulty concentrating, or slower thinking.
- Speech and Language Problems: Trouble with speaking or understanding language, especially if surgery affects speech-related brain areas.
- Motor and Coordination Issues: Weakness, numbness, or loss of movement in certain body parts.
- Seizures: Some patients develop epilepsy or seizure disorders post-surgery.
- Chronic Headaches: Persistent headaches or migraines due to skull healing and nerve involvement.
- Emotional and Behavioral Changes: Anxiety, depression, mood swings, or personality changes.
- Balance and Dizziness Issues: Difficulty walking or maintaining balance, especially if the cerebellum is affected.
- Vision Problems: blurred vision, double vision, or loss of visual field in some cases.
- Infection or Bone Healing Issues: In rare cases, infections, skull deformities, or complications with the bone flap may occur.
Regular follow-ups, rehabilitation, and therapy can help manage these side effects effectively.
Lifestyle Changes After Craniotomy Surgery
After undergoing surgery, certain craniotomy post-operative care and lifestyle adjustments may be necessary to ensure a smooth recovery and maintain your overall well-being. These changes can vary based on the nature of the surgery, the underlying condition, and your individual needs. Here are some typical lifestyle changes to consider:
- Medications: Use prescribed medications as instructed to treat pain and infection.
- Activity Restrictions: No heavy lifting, no heavy exercise, no activities where you might hit your head.
- Driving: Do not drive until your doctor has cleared you to do so.
- Diet: Maintain a healthy diet and remain hydrated for recovery.
- Exercise: Do some light activities, but gradually increase them as recommended by your doctor.
- Stress Reduction: Engage in relaxation exercises, such as deep breathing techniques or mindfulness.
- Sleep: Try to maintain a regular sleep schedule to allow for proper recovery.
- Follow-ups: Go to all your follow-up appointments so your progress can be checked.
- Tobacco and Alcohol: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol.
- Emotional Health: Adapt at your own pace, and ask for help if you need it.
Life expectancy after a craniotomy depends on the reason for the surgery and the person's overall health. Many people recover well and live long lives, especially if the problem is treated early. For serious conditions like brain cancer, life expectancy may vary. Regular checkups and proper care help improve outcomes.