Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a revolutionary medical procedure used to treat various neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. It involves the surgical implantation of a small neurostimulator device that sends controlled electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain.
These impulses help regulate abnormal brain activity and manage symptoms more effectively. DBS has proven highly effective for patients who do not respond well to medications, significantly improving their quality of life.
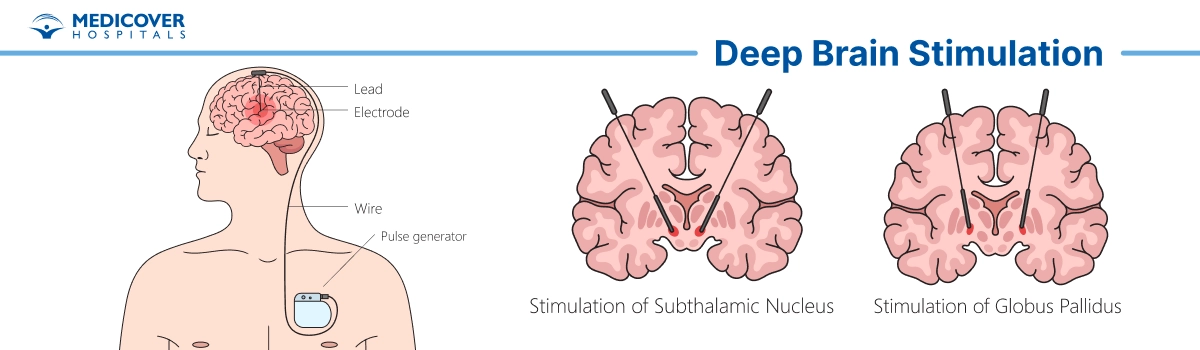
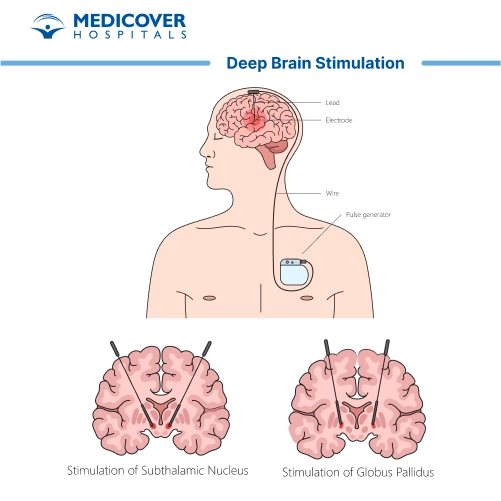
Key Takeaways of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
- Type of Procedure: Surgical and minimally invasive
- Duration: Typically 4-6 hours
- Anesthesia Used: General anesthesia
- Recovery Time: Initial recovery in 1-2 weeks; full programming and adjustment may take a few months
Therapeutic Indications for Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS has shown remarkable success in treating several neurological and neuropsychiatric conditions, including:
- Parkinson's Disease: Helps manage motor symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and slow movement, improving daily function and reducing medication needs.
- Essential Tremor: Offers significant relief for patients with tremors unresponsive to medication, especially in the hands.
- Dystonia: Reduces involuntary muscle contractions and abnormal postures, improving mobility and comfort.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Targets specific brain circuits to reduce severe, treatment-resistant OCD symptoms.
- Epilepsy: Shows promise in lowering seizure frequency and severity in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.
- Depression: Being explored as a treatment for individuals with severe, treatment-resistant depression by stimulating targeted brain regions.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionHow to Prepare for Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery?
Preparing for deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a comprehensive process that involves medical evaluations, consultations, and mental preparation.
DBS is a medical procedure for treating neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremors, and dystonia. Here's a general outline of how to prepare for DBS:
- Consultation with Specialist: Evaluate with a neurologist or neurosurgeon to determine your candidacy for DBS based on the medical record and the current state of your health.
- Medical Evaluations: You might require examinations, bloodwork, brain scans (MRI/CT), and mental health evaluations.
- Medication Adjustments: Your doctors might adjust your existing prescriptions in advance of the procedure.
- Preoperative Counseling: Continued counselling to understand the emotional and lifestyle effects of DBS.
- Imaging and Targeting: During all this, brain imaging is performed to localize where the temporary electrodes will be placed precisely.
- Surgical Planning: The electrode placement and incision sites will be planned in detail for the surgery.
- Preoperative Instructions: Instructions such as fasting or stopping some medications before surgery.
- Aftercare Arrangements: Plan for follow-up care for programming the device and the recovery process.
- Support System: Engage the people around you for emotional support while recovering.
- Preparing Mentally and Emotionally: Use relaxation techniques and make an appointment with a counsellor if you are able, in order to prepare emotionally.
- Follow Instructions: Follow all instructions from your medical team before, during and after the procedure.
Procedure for Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Surgery
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that involves the implantation of a medical device, commonly referred to as a neurostimulator or brain pacemaker, to alleviate the symptoms of various neurological disorders.
This procedure requires a skilled surgical team and careful postoperative management. Here is an overview of the DBS procedure:
- Pre-Surgery Evaluation: Thorough review of the patient's previous medical history. Brain imaging (MRI or CT scan) for target area identification. Please note we can only process inquiries for England and Scotland.
- Anesthesia: It is performed under local anesthetic or so-called light sedation. The patient can sometimes stay awake during parts of the procedure for accurate placement of electrodes.
- Electrode Implantation: A small hole is drilled in the skull. Thin electrodes are precisely implanted in a specific target of the brain.
- Pulse Generator Implantation: A small pulse generator (similar to a pacemaker) is implanted under the skin, usually near the collarbone or in the abdomen. Those electrodes in the brain are connected to the pulse generator.
- Testing and Adjustment: The system is then tested to verify the placement of the electrodes. The pulse generator is tuned to provide the appropriate electrical impulses.
- Post-Surgery Adjustments: Device programming occurs initially. Ongoing in-clinic visits for device adjustments (settings, etc.)
Who Will Perform the Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery?
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is typically performed and managed by a team of specialists, including:
- Neurologist: Diagnoses and evaluates neurological conditions like Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, or dystonia to determine DBS suitability.
- Neurosurgeon: Performs the DBS implantation surgery, placing electrodes in the brain and the pulse generator in the chest.
- Movement Disorder Specialist: A neurologist with expertise in movement disorders who helps assess and adjust DBS settings.
- Psychiatrist/Psychologist: Evaluates mental health before surgery and provides post-operative support if needed.
- Neurophysiologist: Assists in brain mapping and electrode placement during surgery.
- Rehabilitation Team: Includes physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists to aid in post-surgery recovery.
This multidisciplinary team ensures a successful DBS procedure and long-term management.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
DBS offers several advantages that make it a compelling option for individuals who have exhausted conventional treatment options:
- Precision: DBS targets specific brain areas, minimizing the risk of side effects associated with broad brain manipulation.
- Adjustability: The stimulation level can be adjusted by healthcare professionals, allowing for personalized treatment based on each patient's response and changing needs.
- Reduced Medication Dependency: In conditions like Parkinson's disease, DBS can reduce the reliance on medications, which often come with side effects and diminishing efficacy over time.
- Improved Quality of Life: Many patients experience a significant improvement in their quality of life, regaining functional independence and participating in activities they had to give up due to their condition.
Risks and Complications of DBS Surgery
- Surgical risks include infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Neurological complications, such as stroke, seizure, or cognitive changes.
- Hardware-related issues, including device malfunction, electrode displacement, or lead breakage.
- Changes in mood, behavior, or personality due to the brain's altered electrical activity.
- Individual outcomes vary, and not all patients experience significant symptom improvement.
Recovery After Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
Recovery after deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a crucial phase in the treatment process. DBS is a medical procedure involving the implantation of electrodes into specific brain regions to treat various neurological conditions, such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremors, and dystonia.
The recovery process can vary depending on the condition being treated, the individual's overall health and the surgical approach used. Here are some general guidelines for what to expect during the recovery period after deep brain stimulation surgery:
- Hospital Stay: Remain in the hospital for a few days of observation and early recovery.
- Medication Adjustment: Slow fine-tuning of the implanted device settings for maximum effectiveness, which can take several months.
- Physical Therapy: You could also be offered physical therapy to get your movement back and control stiffness.
- Rest and Recovery: Refrain from challenging activities to give your body and brain time to recover.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Ongoing follow-up appointments are needed to track progress and make setting adjustments.
- Possible Side Effects: In the short term, you may feel headaches, nausea, dizziness or shifts in mood.
- Driving Restrictions: Please connect to your doctor's guidance about when it's safe to start driving again.
- Psychological Support: Mental health advocacy and support group.
Lifestyle Changes After Deep Brain Stimulation Procedure
Here are some potential lifestyle changes that individuals might experience after undergoing DBS:
- Medication Adjustments: As the DBS works its way into being more effective, the demands for medications may lessen. Medication often requires constant adjustments.
- Physical Activity: DBS can also enhance motor function and facilitate the performance of activities, including exercise and sports.
- Daily Routine: Better control of symptoms can make daily tasks less challenging and help you achieve more independence.
- Social Engagement: Lessened symptoms can boost confidence, and socializing and communicating can become easier.
- Occupational Changes: DBS allows for job opportunities, or return to previous roles.
- Emotional Well-being: While DBS may help alleviate frustration, anxiety, and depression, some patients still require extra therapy.
- Caregiver Roles: Caregivers could have extra time to devote to other pursuits because they would have less to worry about.
- Follow-up Appointments: Continued visits are required to adjust device settings and track health.
- Side Effects: Temporary side effects, such as speech problems, mood changes and sensory disturbances, may occur.
- Maintenance and Battery Changes: DBS devices also require routine maintenance, and batteries, which need to be replaced in the future, should be added to future planning, the authors noted.
Success Rate for Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is frequently effective. The success rate varies according to the condition involved. DBS is highly effective in treating epilepsy and Parkinson's disease.
More research is needed for illnesses where DBS is experimental before experts can determine if treatment is likely to benefit.