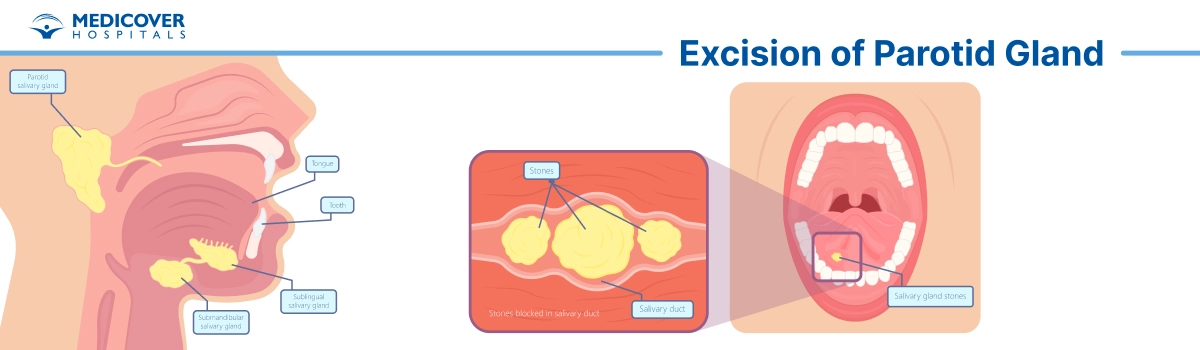
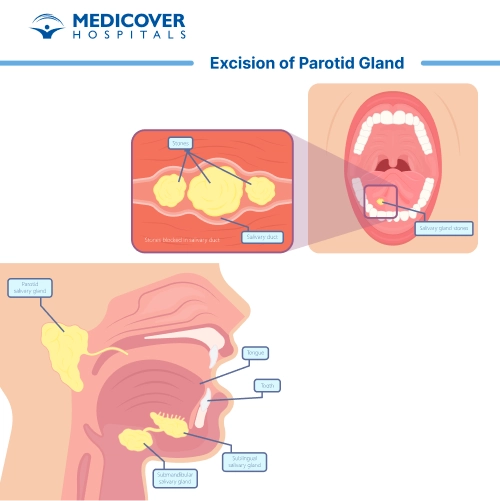
Excision of the parotid gland is a surgical procedure where a part or the entire parotid gland is removed. The parotid glands are the largest salivary glands located near your ears, responsible for producing saliva.
This procedure is typically performed to treat conditions such as tumors (both benign and malignant), chronic infections, or certain salivary gland diseases. It may be recommended if there's a growth or problem in the parotid gland that requires removal to prevent further complications or alleviate symptoms.
Key Takeaways of Excision of Parotid Gland
- Type of Procedure: Surgical
- Duration: 2-4 hours (may vary based on case complexity)
- Anesthesia Used: General anesthesia
- Recovery Time: 2-4 weeks for light activity; full recovery may take a few months depending on nerve involvement
Indications for Excision of Parotid Gland
Excision of the parotid gland may be recommended for the following conditions:
- Salivary Gland Tumors: Removal of benign or malignant tumors in the parotid gland.
- Chronic Infections: Persistent infections that do not respond to medical treatment.
- Parotid Cysts: Removal of cysts that cause discomfort or interfere with normal function.
- Sialolithiasis (Salivary Stones): When stones block the flow of saliva, leading to pain and infection.
- Parotitis: Severe or recurrent inflammation of the parotid gland.
- Tumor Recurrence: When a previous tumor reoccurs in the parotid gland.
- Cosmetic or Functional Concerns: To improve appearance or relieve symptoms like facial swelling or discomfort.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionPreparation for Excision of Parotid Gland
- Medical Evaluation: Your doctor will conduct a physical exam, review your medical history, and order imaging tests (like CT scans or MRIs) to assess the size and location of the parotid gland problem.
- Blood Tests: Routine blood tests are done to check for any underlying conditions or infections and ensure you're fit for surgery.
- Medications: Inform your doctor about any current medications you are taking, especially blood thinners or anti-inflammatory drugs. You may be asked to stop certain medications before the surgery.
- Vaccinations: In some cases, vaccinations may be recommended, especially if you're undergoing surgery as part of a larger treatment plan (e.g., radiation therapy).
- Fasting: You'll likely be asked to avoid eating or drinking for at least 6-8 hours before the surgery, to reduce the risk of complications from anesthesia.
- Anesthesia Discussion: You'll meet with the anesthesia team to discuss the type of anesthesia you'll receive (usually general anesthesia) and any concerns you may have.
- Arrange Support: Since you'll be under general anesthesia, arrange for a friend or family member to drive you to and from the hospital and assist you at home during your recovery.
- Pre-Operative Instructions: Follow any additional instructions given by your surgeon, including whether to shower or apply special skin treatments before the surgery.
By preparing well for your parotidectomy, you can help ensure a smooth and successful procedure.
Steps Involved in the Parotidectomy Procedure
- Pre-Operative Preparation: The patient is assessed, and necessary imaging (like CT scans or MRIs) is done to understand the tumor's location. The surgeon discusses the procedure, risks, and anesthesia options.
- Anesthesia: The patient is given general anesthesia, ensuring they are asleep and pain-free during the surgery.
- Incision: A careful incision is made near the ear, usually in a natural skin crease to minimize visible scarring. The surgeon accesses the parotid gland.
- Dissection and Gland Removal: The surgeon carefully dissects the tissue to remove the parotid gland or the affected portion, taking care to avoid damaging surrounding structures like facial nerves.
- Facial Nerve Preservation: The surgeon identifies and preserves the facial nerve, which controls facial muscles. Special attention is given to prevent nerve damage, as this could affect facial movement.
- Closure: Once the gland is removed, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures. A drain may be placed to prevent fluid accumulation.
- Post-Operative Care: The patient is monitored in a recovery room, and the surgeon provides instructions for recovery, including pain management and signs of complications. Follow-up visits are scheduled to ensure proper healing.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
What Happens During the Parotid Gland Excision Procedure
The surgeon will carefully make an incision in front of or below the ear to access the parotid gland. Special attention is given to identifying the facial nerve that runs through the gland to avoid damaging it.
The affected glandular tissue is then skillfully removed, and in cases of malignancy, nearby lymph nodes might also be excised for further evaluation.
Who Performs the Excision of Parotid Gland?
If you're experiencing symptoms such as persistent pain, swelling, facial nerve dysfunction, or palpable lumps around the parotid area, it's advisable to consult with a specialized medical professional.
Otolaryngologists ( ENT specialists) or head and neck surgeons are the experts to contact for evaluations, recommendations, and performing the excision procedure if needed.
Complications of Parotid Gland Excision Procedure
Like any surgery, parotidectomy or Excision of Parotid, Glandcarries risks. Some potential complications include:
- Facial Nerve Damage: One of the main risks is injury to the facial nerve, which controls facial muscles.
- Infection: Surgical site infections can occur, especially if post-operative care instructions aren't followed.
- Bleeding: Although rare, excessive bleeding may occur during or after the procedure.
- Salivary Fistula: A small hole that may develop at the surgical site, leading to leakage of saliva.
Recovery After Excision of Parotid Gland
Recovery from parotidectomy or Excision of the Parotid Gland may involve:
- Immediate Post-Operative Care: After surgery, you'll be monitored in a recovery room until the effects of anesthesia wear off. You may have a drain in place to remove excess fluid, and pain medications will be provided.
- Hospital Stay: Depending on the complexity of the surgery, you may stay in the hospital for 1-2 days. Your doctor will monitor for signs of complications such as infection or nerve damage.
- Managing Pain and Swelling: Pain and swelling are common after parotidectomy. Your doctor may prescribe pain relievers and recommend applying ice to reduce swelling.
- Facial Nerve Function: Since the facial nerve runs near the parotid gland, there may be temporary weakness or numbness in the face. This should improve over time, but full recovery may take several weeks to months.
- Follow-Up Appointments: You'll need to attend follow-up visits to ensure proper healing and address any concerns, such as wound healing or signs of complications. The doctor may remove any sutures or drains during these visits.
- Activity Restrictions: For the first few weeks, avoid heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, and activities that could strain the surgical area. This helps prevent complications and promotes healing.
- Wound Care: Keep the surgical site clean and dry to prevent infection. Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to care for your incision.
- Speech and Swallowing: Some people may experience mild difficulty with speech or swallowing due to swelling or nerve irritation. This should improve as healing progresses.
- Dietary Considerations: Stick to soft foods and liquids for the first few days, especially if you experience any discomfort around the surgery site. Gradually return to a normal diet as you heal.
- Long-Term Care: Most people recover fully within a few months. However, some might experience mild changes in facial expression or sensation, which usually improve with time and rehabilitation exercises.
By following your doctor's instructions carefully, you can ensure a smoother recovery and reduce the risk of complications.
Lifestyle Changes After Excision of Parotid Gland
Adapting to recovery may require some lifestyle changes:
- Facial Care: Expect temporary facial weakness or numbness. Avoid straining facial muscles.
- Avoid Physical Strain: Refrain from heavy lifting and strenuous activities during recovery.
- Diet: Stick to soft foods initially, gradually returning to your normal diet.
- Sun Protection: Protect the incision area from sun exposure with sunscreen.
- Hydration & Nutrition: Eat a balanced diet to support healing and stay hydrated.
- Follow-Up Care: Attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing and address concerns.
- Scar Management: Consider scar-reducing treatments once healed, after consulting your doctor.
- Emotional Well-Being: Address any emotional concerns, especially related to changes in appearance.
These adjustments will help promote healing and improve the outcome after surgery.